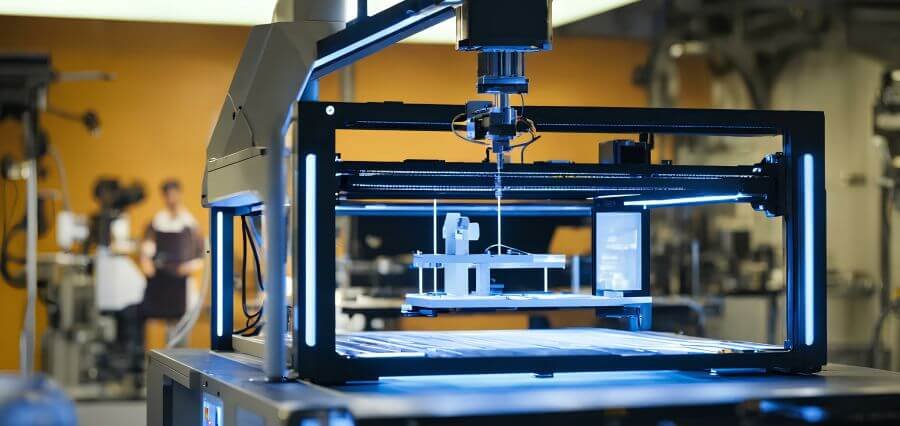
In the advancing sector of manufacturing, additive manufacturing (AM), commonly known as 3D printing, is emerging as a groundbreaking force that is reshaping the production paradigm. By building objects layer by layer from digital models, this technology is not just enhancing the efficiency and flexibility of manufacturing processes but also enabling unprecedented levels of innovation and customization across various industries.
A Paradigm Shift in Production
Traditional manufacturing methods, such as subtractive manufacturing, involve cutting away material from a solid block to create a final product. This approach, while effective, often results in significant material waste and limits the complexity of designs that can be produced. Additive manufacturing, on the other hand, constructs objects by adding material only where it is needed, minimizing waste and allowing for the creation of complex geometries that would be impossible or prohibitively expensive to achieve using conventional methods.
This shift from subtractive to additive processes represents a fundamental change in how products are conceived, designed, and produced. It enables manufacturers to move away from the constraints of traditional production lines and towards more agile, responsive manufacturing systems that can adapt to changing demands with ease.
Driving Innovation Across Industries
The impact of additive manufacturing is being felt across a wide range of industries, from aerospace and automotive to healthcare and consumer goods. In aerospace, for instance, 3D printing is enabling the production of lightweight, high-strength components that reduce fuel consumption and emissions. Companies like Boeing and Airbus are using AM to produce complex parts that were previously unachievable, thus improving performance and reducing costs.
In the automotive industry, additive manufacturing is accelerating the development of prototypes and custom parts. Ford, for example, has integrated 3D printing into its production process to quickly produce and test new components, reducing development time and enabling faster time-to-market for new models.
Healthcare is another sector where additive manufacturing is making a significant impact. Custom implants, prosthetics, and even bioprinted tissues are being developed using 3D printing technology. Surgeons can now create patient-specific models to plan complex surgeries with greater precision, improving outcomes and reducing risks.
The Benefits of Additive Manufacturing
One of the most significant advantages of additive manufacturing is its ability to produce highly customized products at scale. Whether it’s a custom-fit medical implant or a personalized consumer product, 3D printing allows for a level of customization that was previously unattainable. This capability is particularly valuable in industries like healthcare, where patient-specific solutions can lead to better outcomes.
Additive manufacturing also offers environmental benefits. By using only the material needed to create a part, 3D printing reduces waste and conserves resources. Moreover, the ability to produce parts on-demand, rather than in large batches, reduces the need for warehousing and inventory, further lowering the environmental footprint of manufacturing operations.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its many advantages, additive manufacturing is not without its challenges. Material limitations, particularly in metals, remain a significant hurdle. While advances are being made, the range of materials that can be used in 3D printing is still limited compared to traditional manufacturing methods. Additionally, the speed of 3D printing processes needs to improve for it to compete with mass production techniques.
However, ongoing research and development are addressing these challenges. Innovations in materials science are expanding the range of printable materials, while improvements in printing speed and precision are making additive manufacturing more viable for large-scale production. As these advancements continue, the adoption of 3D printing is expected to accelerate, further revolutionizing the manufacturing landscape.
Conclusion
Additive manufacturing is more than just a technological advancement; it is a transformative force that is revolutionizing how products are designed, developed, and produced. By enabling greater customization, reducing waste, and driving innovation across industries, 3D printing is poised to reshape the future of manufacturing. As the technology continues to evolve, it will unlock new possibilities for designers, engineers, and manufacturers, leading to a more efficient, sustainable, and innovative production ecosystem.