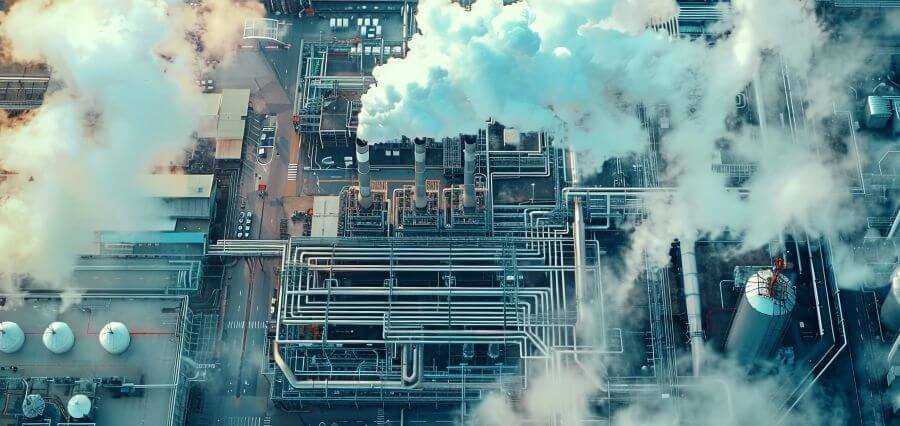
The global manufacturing landscape is undergoing a significant shift as companies increasingly consider reshoring—bringing manufacturing operations back to their home countries. This trend, driven by factors such as geopolitical tensions, supply chain disruptions, and rising labor costs in traditional offshore locations, is prompting Asian manufacturing hubs to adapt and evolve. In this article, we explore how these hubs are responding to the reshoring movement, ensuring they remain competitive in the changing global market.
The Reshoring Phenomenon
Reshoring has gained momentum in recent years as companies reassess the risks and benefits of offshore manufacturing. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted vulnerabilities in global supply chains, leading many businesses to reconsider their reliance on distant manufacturing bases. Additionally, increasing trade tariffs, rising labor costs in Asia, and a growing emphasis on sustainability are driving companies to explore reshoring as a viable alternative.
For Asian manufacturing hubs, which have long been the backbone of global production, these trends present both challenges and opportunities. To remain relevant, these hubs are adopting innovative strategies, investing in technology, and exploring new business models.
Embracing Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
One of the key ways Asian manufacturing hubs are adapting to reshoring trends is by embracing advanced manufacturing technologies. Automation, robotics, and artificial intelligence are being integrated into production processes to enhance efficiency and reduce costs. By leveraging these technologies, manufacturers in Asia can compete with reshored operations that benefit from lower labor costs in their home countries.
Smart Factories: The concept of smart factories is gaining traction across Asia. These factories utilize IoT devices, sensors, and real-time data analytics to optimize production processes. By implementing smart manufacturing practices, Asian hubs can improve productivity, minimize waste, and reduce lead times, making them more attractive to global companies seeking to balance cost and efficiency.
Additive Manufacturing: Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, is another technology that Asian manufacturers are adopting to stay competitive. This technology allows for the production of complex, customized components with minimal material waste. By integrating additive manufacturing into their operations, Asian hubs can offer greater flexibility and quicker turnaround times, addressing the demand for localized and customized production.
Diversifying Supply Chains
In response to the reshoring movement, Asian manufacturing hubs are diversifying their supply chains to reduce dependency on a single market. This strategy involves expanding their customer base, exploring new markets, and establishing regional production facilities closer to end consumers.
Regionalization of Production: Some Asian manufacturers are setting up regional production facilities in key markets such as Europe and North America. By doing so, they can reduce shipping costs, shorten lead times, and mitigate the risks associated with long supply chains. This approach also allows them to better serve customers who prioritize sourcing from nearby locations due to sustainability concerns or geopolitical factors.
Multi-Sourcing Strategies: To counter the impact of reshoring, Asian manufacturers are adopting multi-sourcing strategies. Instead of relying on a single supplier or location for critical components, they are establishing relationships with multiple suppliers across different regions. This diversification reduces the risk of supply chain disruptions and ensures a steady flow of materials, even in times of crisis.
Enhancing Sustainability Practices
As sustainability becomes a key consideration for businesses worldwide, Asian manufacturing hubs are stepping up their efforts to meet environmental standards and appeal to eco-conscious companies. By adopting sustainable practices, these hubs can attract businesses that prioritize responsible sourcing and environmental stewardship.
Green Manufacturing: Asian manufacturers are investing in green technologies and processes to reduce their environmental footprint. This includes adopting renewable energy sources, implementing waste reduction programs, and improving energy efficiency in their operations. By positioning themselves as leaders in green manufacturing, Asian hubs can appeal to companies that value sustainability and are looking to reduce their carbon footprint.
Circular Economy Initiatives: The circular economy model, which focuses on reducing waste and reusing materials, is gaining traction in Asia. Manufacturers are exploring ways to incorporate recycled materials into their production processes and design products that are easier to disassemble and recycle. These initiatives not only contribute to sustainability but also create new business opportunities in recycling and remanufacturing.
Strengthening Resilience Through Innovation
Innovation is at the core of how Asian manufacturing hubs are adapting to reshoring trends. By continuously innovating, these hubs can enhance their resilience and remain competitive in the global market.
Investing in Research and Development (R&D): Asian manufacturers are increasing their investment in R&D to develop new products, improve existing processes, and explore emerging technologies. This focus on innovation enables them to stay ahead of the curve and offer cutting-edge solutions to global customers.
Collaboration and Partnerships: Collaboration is becoming increasingly important as Asian hubs seek to adapt to changing market dynamics. Manufacturers are forming partnerships with technology providers, research institutions, and other industry players to share knowledge, develop new technologies, and explore new markets. These collaborations foster innovation and help manufacturers respond more effectively to the challenges posed by reshoring.
Conclusion
As the reshoring trend gains momentum, Asian manufacturing hubs are demonstrating remarkable adaptability and resilience. By embracing advanced technologies, diversifying supply chains, enhancing sustainability practices, and fostering innovation, these hubs are positioning themselves to remain key players in the global manufacturing landscape. While the challenges posed by reshoring are significant, the strategies being adopted by Asian manufacturers highlight their commitment to staying competitive and relevant in a rapidly evolving industry.